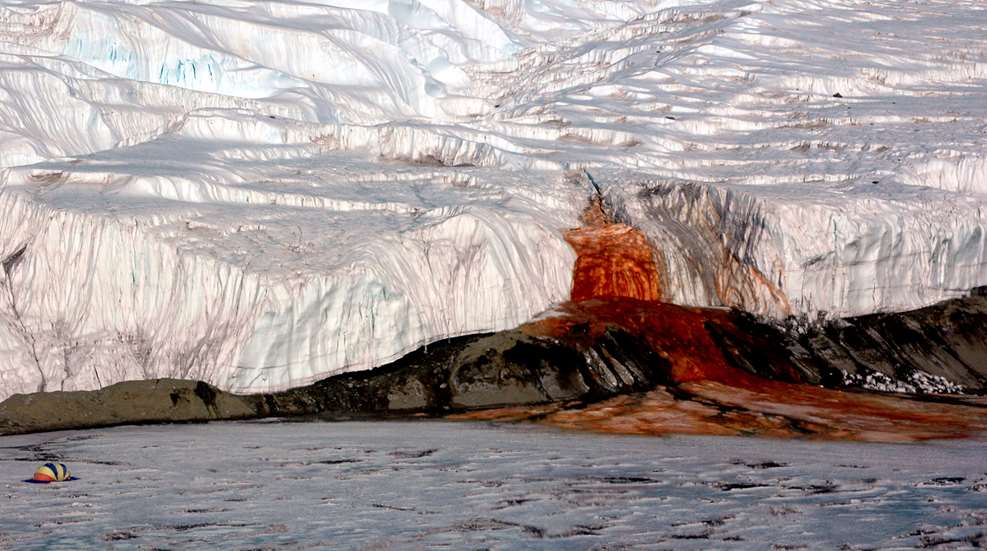
Antarctica’s McMurdo Dry Valley is part of the one percent of Antarctica that is not covered by ice. However, a subglacial lake occasionally spews red liquid out of the fissures in the Taylor glacier. This waterfall of blood-colored liquid has puzzled scientists for years. But while this natural phenomenon is certainly spooky, it’s not Mother Nature’s time of the month or a vampire’s lair.
McMurdo Dry Valley is an extremely interesting and unique locale in Antarctica. It’s full of craggy mountains, and high winds and grit have carved rocks into unusual shapes to rival the sculptures of Beetlejuice’s Saturn. This unusual and desolate place sets the scene for the shock value of Blood Falls.
Blood Falls was first documented by Australian geologist Griffith Taylor in 1911. He incorrectly assumed that red algae was responsible for its creepy color. However, the true reason behind the red water wouldn’t be proven until 2017. For decades Blood Falls was just an ominous mystery.
The water flowing from the glacier is twice as salty as seawater, which is why it can freely flow in temperatures below freezing. Its salinity also means that it cannot be glacial runoff, because glaciers are comprised of fresh water. Therefore, scientists needed to find the true source of the flowing liquid. That’s when they found a salt lake hidden underneath 1,312 feet of ice.
This perfectly preserved 5-million-year-old lake is rich in iron, just like blood. When the iron-rich brine breaks free of its icy subglacial prison, it interacts with oxygen. Once oxygenated, the iron rusts, giving the water a reddish-brown color that looks remarkably like blood. While this scientific reasoning is astounding and also comforting, the real spookiness lies beneath the ancient ice.
Microorganisms still live in the brine, surviving in extreme conditions of low temperatures and salty water. These mysterious signs of life are still being studied by scientists. For even more surprising signs of life in unlikely places, check out the Door to Hell.